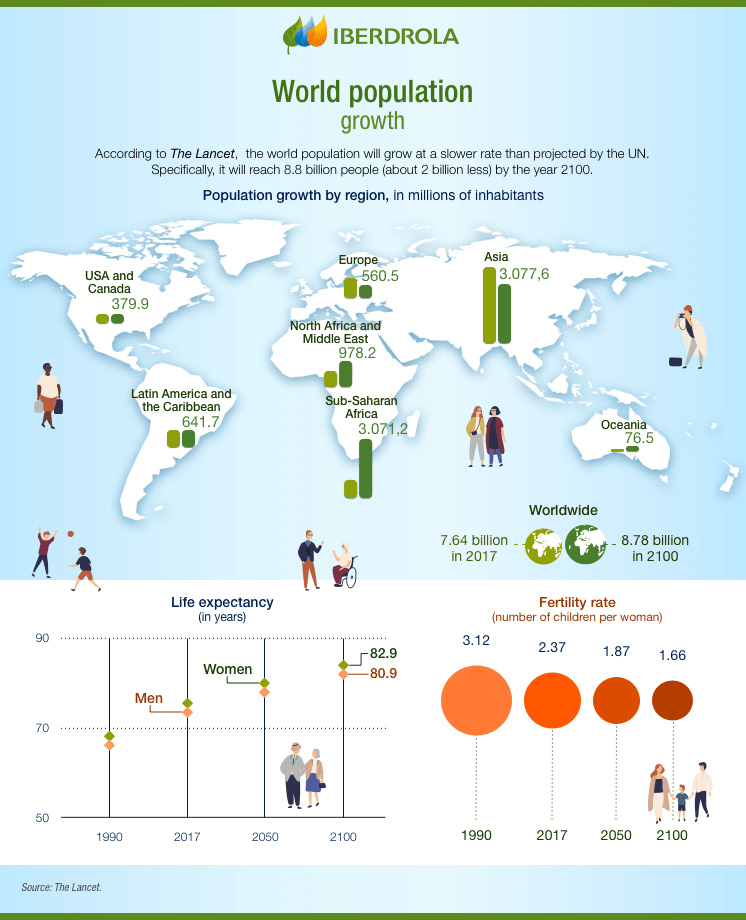
WORLD POPULATION DYNAMICS
These ratios show if a population is increasing or decreasing.
HOW DO WE STUDY POPULATION DYNAMICS?
To calculate the number of people living in a place we use:
- NATURAL POPULATION MOVEMENT is the difference between the births and deaths.
- MIGRATORY MOVEMENT represents the movement of people and is calculated resting the immigration from the emigration figures. (People coming from abroad and people leaving the country to live abroad). This is called net migration rate
NATURAL POPULATION MOVEMENTS: BIRTHS
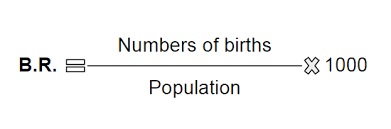

Births are the number of children born in a place in a year. To analyze this factor, we take into consideration:
- BIRTH RATE is the number of births in relation to the total population multiplied by 1000. So, it is expressed in per mile (%0).
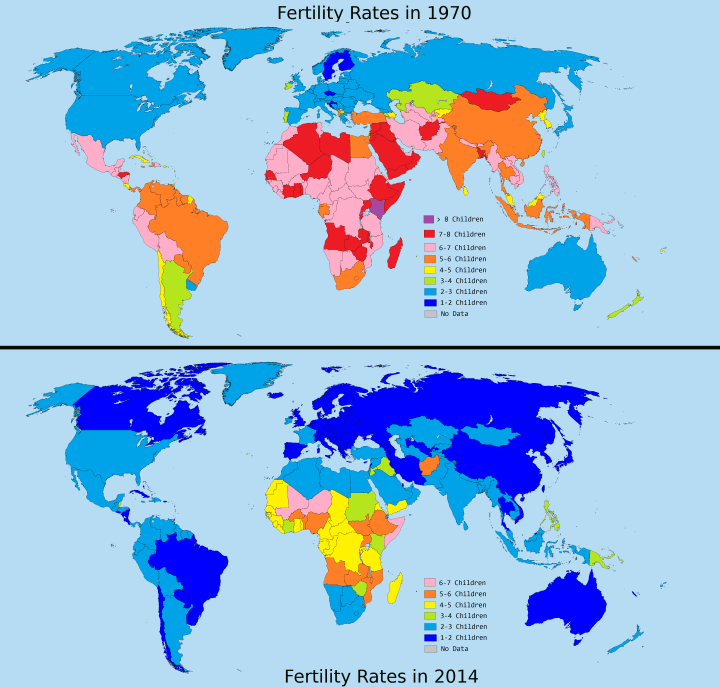
- FERTILITY RATE represents the number of live births per women aged 15 -49 expressed in per mile.
- AVERAGE NUMBER OF CHILDREN PER WOMAN is used to know if a generation could be replaced by the next one. An average of 2.1 children per women ensures that replacement.

NATURAL POPULATION MOVEMENTS: DEATHS
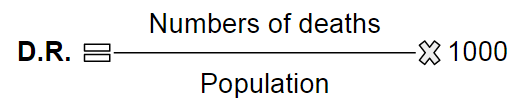
Deaths are the number of died people in a place in a year. To analyze this factor, we consider:
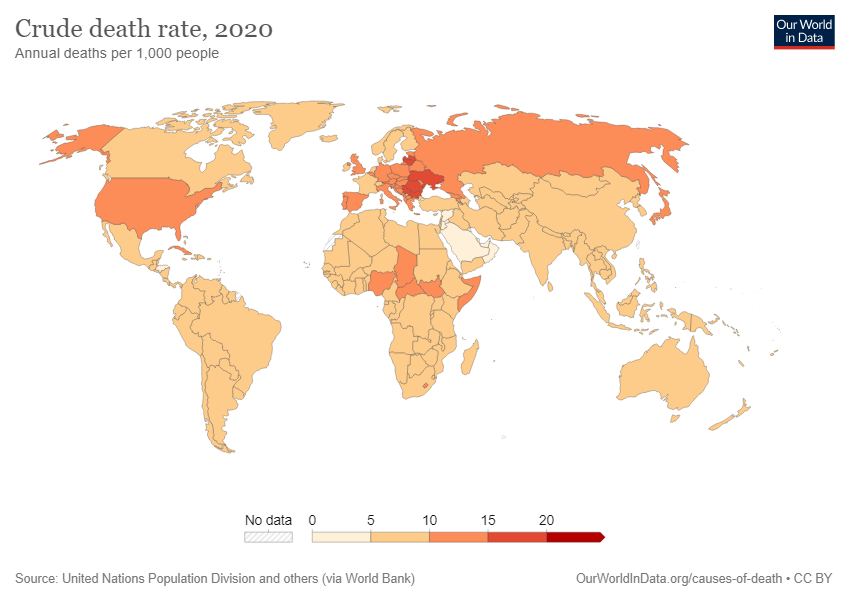
1 DEATH RATE or number of deaths in relation to the total population multiplied by 1000, expressed in per mile.
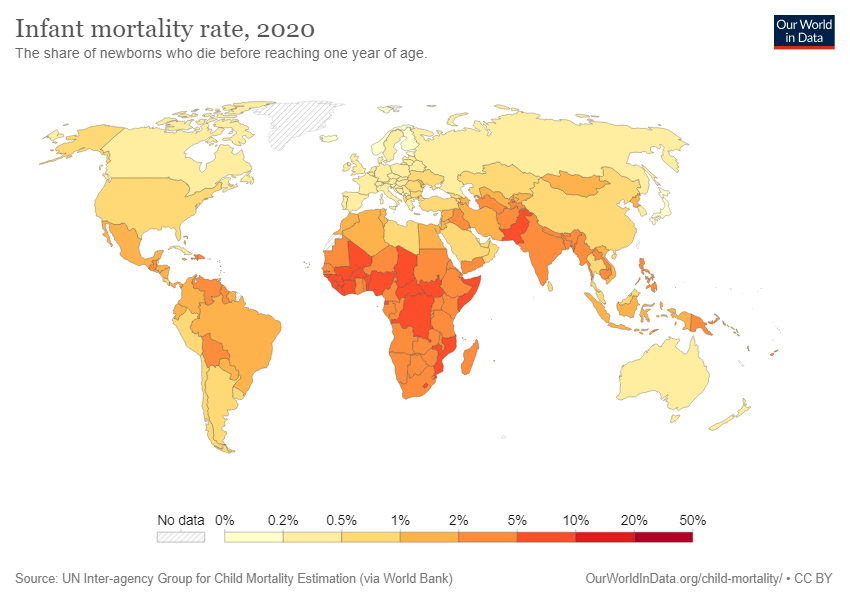
2 INFANT MORTALITY RATE calculates the number of dead babies before their first birthday in a place during a year multiplied by a 1000.
3 LIFE EXPECTANCY is the average age a person is expected to live at birth.

NATURAL POPULATION GROWTH
NATURAL POPULATION GROWTH is the difference between the number of births and deaths.
NATURAL POPULATION GROWTH RATE It also can be calculated using the birth and death rates. This is measure in a percentage(%) You get the percentage by dividing the difference between the birth and death rates by 10.
If the natural growth is positive, the population grows but , when the result is negative, it decreases. If the difference equals zero, then population growth is zero.

MIGRATIONS
It is the movement of people from a place to another. Factors affecting migrations are: distance, duration and decision.
According to distance, migrations could be classified into:
- REGIONAL MIGRATION is a move within a country.
- INTERNATIONAL MIGRATION is a move between country.
According to duration we distinguish two types of migration:
- TEMPORATY MIGRATION is a move that lasts less than a year.
- PERMANENT MIGRATION is a move where the migrant expects to stay in the new location.
Decision applied to migration means why a person migrated. Related to this there are two types of migration:
- VOLUNTARY MIGRATION is a move by choice
- FORCED MIGRATION is a move against the migrant´s will due to natural hazards, political or religious persecution, etc.

Emigrant is a person moving out of a country.
Migrant is the person during the moving.
Immigrant is a person moving into a country.
Migrations affect in population growth through migration balance. Migration balance is the difference between the number or persons having entered in a territory and the number of persons having left the territory in the course of a year
A PLANET WITH TWO DIFFERENT POPULATION DYNAMICS
Population dynamics change along time as well depending on the economic and social development.
- LESS ECONOMICALLY DEVELOPED COUNTRIES present a high natural population growth. Africa has the fastest population growth.
LIFE EXPECTANCY is increasing due to better health conditions and the decrease in infant mortality.
- DEVELOPED COUNTRIES have a lower natural population growth due a drastic fall in the fertility rates and the ageing population. Life expectancy is high.

POWERPOINT PRESENTATION:
NOTES READY TO STUDY:
WORKSHEETS TO PRACTICE:
1 Population and Settlement worksheet
population_calculation_worksheet
VIDEOS TO REVIEW:

